ICM 48320 1/48 Martin B-26B Marauder
B-26B Marauder
WWII American Bomber
American twin-engine medium bomber B-26, manufactured by the Glenn L. Martin Company, was designed and created in 1939 under the requirements of the US Army Air Corps for a new high-speed medium bomber. Initially, the project was called Model 179. The construction of production aircraft was started without the usual stage of a prototype or pre-series samples.
The first B-26 flew on November 25, 1940, and it was adopted by US aviation in February 1941. Structurally, the B-26 Marauder was a high-wing with a spacious fuselage and a crew of five (in later versions up to seven) people. During operation, the design of the bomber was constantly changed to improve flight and combat characteristics. Since 1943, the wing area and keel were increased, with these changes, the aircraft was produced until the end of production.
The last modification of the B-26B Marauder (B-26B-55-MA) was produced until February 1944; these aircraft took an active part in US bomber operations in Europe at the final stage of World War II. B-26B Marauder aircraft are known as one of the most famous US bombers during the Second World War.
Markings
B-26B-55MA 42-96077 "Ladies Delight", 584th Bomb Squadron, 394th Bomb Group, Summer 1944
B-26B-55MA 42-96214 "Coral Princess III", 494th Bomb Squadron, 344th Bomb Group, 1944
B-26B-55MA 42-96165 "The Big Hairy Bird", 599th Bomb Squadron, 397th Bomb Group, July 1944
Model size (length x width)
387 х 454 mm

Airfix A02043V 1/72 F-80C Shooting Star
F-80C Shooting Star
Initially developed around the British Halford H.1 engine taken from the de Havilland Vampire prototype, the project advanced under the strictest secrecy, with a team from 'Skunk Works' producing an airframe in an impressive 143 days. It is reported that two operational sorties were flown by the jet during WWII, however, these were non-combat missions and of a highly classified nature.
The development of the Shooting Star leant heavily on early jet technology supplied by the British, as the Americans were lagging behind both Britain and Germany regarding jet propulsion and the discovery of the Luftwaffe's Messerschmitt Me 262 highlighted the need for their own viable jet fighter. Initially developed around the British Halford H.1 engine taken from the de Havilland Vampire prototype, the project advanced under the strictest secrecy, with a team from 'Skunk Works' producing an airframe in an impressive 143 days. The Shooting Star showed great promise during testing, attaining a speed of 500mph in level flight, the first turbojet powered USAAF aircraft to do so.
Produced just too late to see combat during WWII, it is interesting to note that two pre-production Shooting Stars were sent to England during WWII for familiarisation purposes, with a further two sent to Italy with the 1st Fighter Group at Lesina. It is reported that two operational sorties were flown by the jet during WWII, however, these were non-combat missions and of a highly classified nature. The F-80C would be used extensively during the Korean War, where the aircraft would equip ten USAAF fighter/fighter bomber squadrons and one reconnaissance unit, but by then, this elegant early jet was already beginning to be outclassed. By the end of its production run, over 1700 Shooting Stars of all variants had been produced.
Includes
- Sprues
- Decals
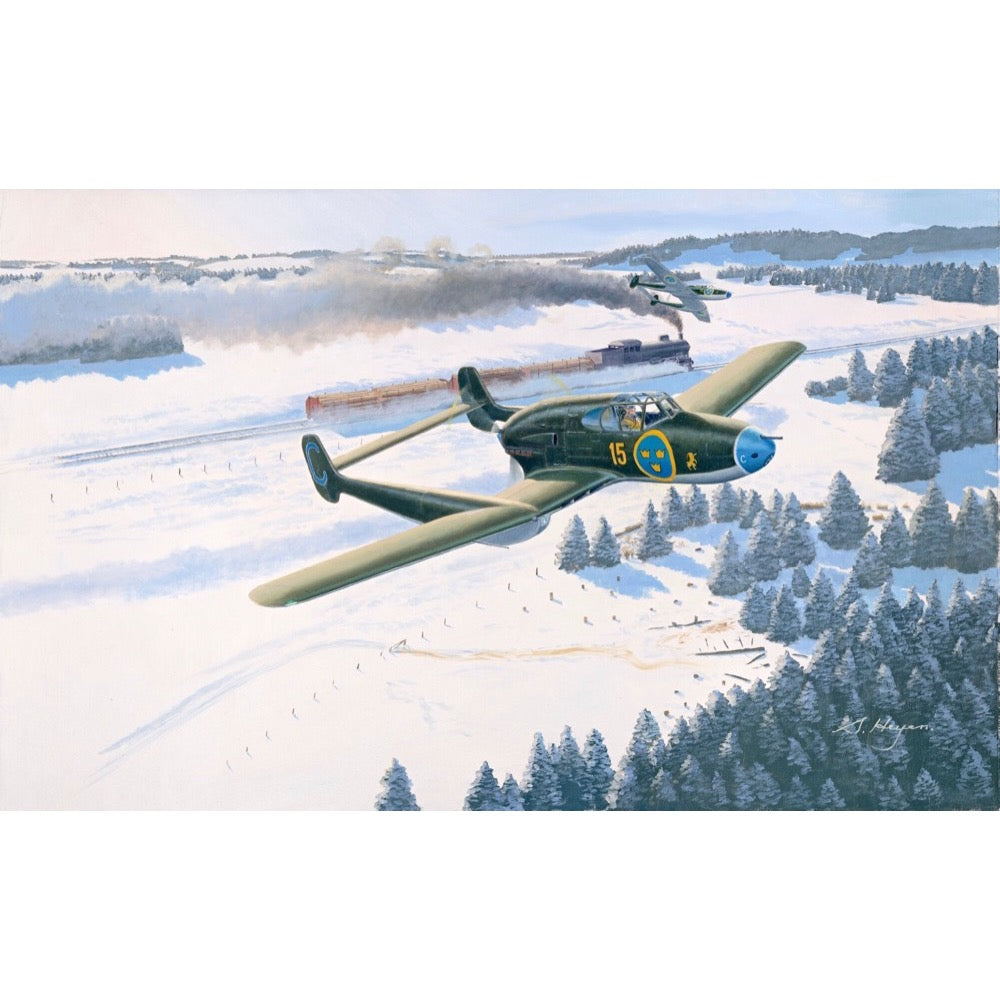

Pilot Replicas 48A001 1/48 Saab J21 A3 Injection Molded Pe Parts and Cartograf Decals
Top quality plastic kit with surface details 2nd to none. Photo etched detail parts included. Decals printed by Cartograf.
In early 1941, Saab and the aircraft designer Frid Wänström accompanied by his team, started the study of a new fighter for the Swedish Airforce.This new fighter utilized the powerful German engine DB 605B as a pusher mounted between twin booms.The pushing propeller however, created a need for the designers to develop an ejection seat, which made the J21 one of the first fighter aircraft in production to be fitted with an ejection seat.
The J21 was Sweden's first fighter aircraft with ”tricycle landing gear”.The heavy armament of one 20mm cannon was mounted in the nose together with two 13mm machine guns, and two 13mm machine guns were mounted in the wings.This provided provided several key advantages.
The first J21A took flight in July 1943 with SAAB chief test pilot Claes Smith at the controls which was followed by operational service into late 1945.
A total of 297 J21 aircrafts fitted with theV-12 engine were delivered from 1945 in 3 versions,21A-1,A-2 and A-3.This kit depicts the J21A-3 version which utilized updated machine guns and a cannon made from Bofors. The updated J-21 also carried rockets and bombs and included other updates.
The performance on the V-12 powered J21 was generally good with very tight turning circle on low altitudes while featuring heavy and concentrated firepower from the massive guns. Limitations were with poor rearward visibility and heavy controls, making air combat tiring.
The SAAB J 21A was phased out from service after 1954 with most of the airforce aircrafts being replaced with the jet-powered deHavilland J28 Vampire and SAAB J29 Flying barrel.